Pumps are classified according to their working principles:
1. Vane pump
Vane pumps can be divided into: centrifugal pumps, mixed flow pumps, axial flow pumps, and vortex pumps.
Centrifugal pumps can be divided into single-stage pumps and multi-stage pumps.
Single-stage pumps can be divided into: single-suction pump, double-suction pump, self-priming pump, non-self-priming pump, etc.
Multi-stage pumps can be divided into: segment type and volute type.
Mixed flow pumps can be divided into volute type and guide vane type.
Axial flow pumps can be divided into fixed vanes and adjustable vanes.
Vortex pumps can also be divided into single suction pumps, double suction pumps, self-priming pumps, non-self-priming pumps, etc.
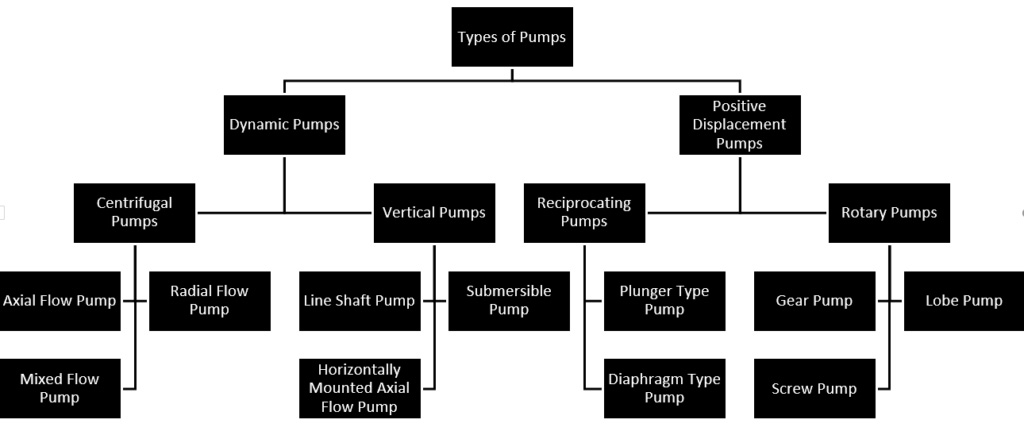
2. Positive displacement pump
Positive displacement pumps can be divided into reciprocating pumps and rotor pumps.
Positive displacement pumps rely on working elements to reciprocate or rotate in the pump cylinder to alternately increase and decrease the working volume to achieve the suction and discharge of liquid. Positive displacement pumps with reciprocating working elements are called reciprocating pumps, and rotary pumps are called rotary pumps. The suction and discharge processes of the former are carried out alternately in the same pump cylinder, and are controlled by the suction valve and the discharge valve; the latter is through the rotation of working elements such as gears, screws, vane rotors or sliding vanes to force liquid from the suction The side shifts to the discharge side.
The flow rate of the positive displacement pump at a certain speed or the number of reciprocations is constant, and it hardly changes with the pressure; the flow and pressure of the reciprocating pump have large pulsation, and corresponding measures to reduce pulsation need to be taken; the rotary pump generally has no pulsation or only small Pulsation; With self-priming ability, the air in the pipeline can be sucked into the liquid after the pump is started; the discharge pipeline valve must be fully opened when the pump is started; the reciprocating pump is suitable for high pressure and small flow; the rotary pump is suitable for small and medium flow And higher pressure; reciprocating pump is suitable for conveying clean liquid or gas-liquid mixture. In general, the efficiency of positive displacement pumps is higher than that of power pumps.
3. Jet pump
The fluid is ejected by a high-speed jet generated by the working fluid, and then the energy of the ejected fluid is increased through momentum exchange.
Power pumps rely on the force of the rapidly rotating impeller on the liquid to transfer mechanical energy to the liquid to increase its kinetic energy and pressure energy, and then through the pump cylinder, most of the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy to achieve delivery. Power pumps are also called impeller pumps or vane pumps. Centrifugal pumps are the most common power pumps.
The head produced by the power pump at a certain speed has a limit value, and the head changes with the flow; the work is stable, the delivery is continuous, the flow and pressure are not pulsating; generally there is no self-priming ability, the pump needs to be filled with liquid or the pipeline is pumped It can only start to work after it becomes a vacuum; it has a wide range of applicable performance; it is suitable for transporting clean liquids with small viscosity. The specially designed pump can transport mud, sewage, etc. or water transport solids. Power pumps are mainly used for water supply, drainage, irrigation, process liquid transportation, power storage, hydraulic transmission, and ship jet propulsion.
4. Other classifications of water pumps
In addition to the classification according to the working principle, the pump can also be classified and named according to other methods. For example, according to the driving method, it can be divided into electric pump, steam turbine pump, diesel engine pump and water turbine pump; according to the structure, it can be divided into single-stage pump and multi-stage pump; according to the purpose, it can be divided into boiler feed water pump and metering pump, etc.; according to transportation The properties of liquids can be divided into water pumps, oil pumps and mud pumps.
The pump can also be divided into:
1) Vertical pump
2) Horizontal pump
Divided by the number of suction ports:
1)) Single suction pump
2)) Double suction pump
According to the prime mover driving the pump:
1) Electric pump
2) Steam turbine pump
3) Diesel engine pump
4) Water turbine pump
Other types of pumps refer to a type of pumps that transfer energy in another way. For example, a jet pump relies on high-speed injection of working fluid, sucks the fluid that needs to be transported into the pump, and transfers energy by mixing the two fluids for momentum exchange; the water hammer pump is produced when the flowing water is suddenly braked Energy makes part of the water pressure rise to a certain height; the electromagnetic pump makes the energized liquid metal flow under the action of electromagnetic force to achieve delivery; the gas lift pump sends compressed air or other compressed gas to the liquid through the pipe At the bottom layer, make it form a lighter gas-liquid mixed fluid, and then use the pressure of the liquid outside the tube to pressure the mixed fluid up.
Post time: 2021-12-07











